交通运输考研复试笔试整理

交通运输考研复试笔试整理
Yusialone交通工程笔试复试知识点整理
1. 单向交通的设置条件
- 具有起终点相同的两条平行道路,距离在350-400m以内
- 具有明显潮汐特征的街道,宽度不足三车道可以实施可逆性单向交通
- 复杂的多路交叉口,某些方向交通另有出路的,才可将相应的进口改成单向交通
2. 公共交通优先措施
公交优先设施
- 公交专用道(通过标志划分一条或多条车道给公交车专用)
- 公交专用进口道
- 换乘衔接系统:地铁换乘等
- 大容量快速交通公交系统
公交优先管理
- 补贴政策
- 扶持政策
- 限制小汽车出行
公交优先控制
- 调整信号相位方案
- 增加公交车通行次数
- 使用公交车感应信号
3. 出行分布的类型及其特点和适用条件
出行分布是交通规划四阶段模型中的重要环节,用于描述各交通小区之间出行量的大小。
增长系数法
- 特点:简单易懂,计算方便,基于现状出行分布进行预测
- 缺点:对现状出行分布依赖性强,未考虑出行成本对分布的影响
- 适用条件:
- 交通系统变化不大,各小区之间的交通联系相对稳定
- 主要用于短期预测,未来交通状况与现状相似
重力模型
- 特点:考虑了交通小区规模(人口或就业岗位)和出行成本(时间、距离或费用),模型参数可根据实际数据标定
- 缺点:参数标定需要大量出行调查数据,出行成本衡量可能不够准确
- 适用条件:
- 城市或区域层面的出行分布预测
- 有较为详细的交通小区规模和出行成本数据
4. 慢行交通一体化的认识
理念层面
- 健康出行:鼓励人们选择步行、自行车等健康环保的出行方式,提高身体素质,减少空气污染
- 可持续出行:减少对小汽车的依赖,降低能源消耗和温室气体排放
- 宜居城市:通过营造良好的慢行交通环境,提升城市吸引力,增强居民幸福感
系统层面
- 完善的慢行交通网络:连续的步行道、自行车道、过街设施等,确保安全性和可达性
- 舒适的慢行交通环境:绿化、遮阳、休息设施等,提高舒适性和吸引力
- 智能化的慢行交通管理:智能导航、共享单车管理、交通信息发布等
挑战层面
- 资金投入不足:慢行交通设施建设需要大量投入但往往被忽视
- 规划设计不合理:缺乏系统性,导致网络不连续、不安全
- 管理维护不到位:设施维护不及时,影响使用效果
5. 新建道路过程及交通工程学原理的应用
建设过程
- 交通需求分析与规划:通过交通调查和需求预测,确定道路功能定位和等级
- 道路选线与设计:考虑地形、环保、拆迁、土地利用等因素进行选线,进行几何设计、路面结构设计和交通工程设施设计
- 道路施工:场地平整、路基施工、路面施工、交通工程设施施工和排水工程施工
- 道路运营与维护:实施交通管理、监控、信息发布等措施,进行日常维护和定期检查
交通工程学原理的应用
- 交通流理论:指导道路容量分析和交通运行评价
- 交通安全理论:指导安全设施设计和危险点治理
- 交通经济学理论:指导投资决策和效益评估
6. 停车诱导系统的认识
意义
- 缓解城市拥堵:引导驾驶员快速找到车位,减少寻找停车位的交通量
- 提高效率:节省驾驶员寻找停车位的时间,提高停车资源利用率
- 改善环境:减少尾气排放和能源消耗
- 提升城市形象:体现城市智能化管理水平
系统类型
- 静态与动态诱导系统
- 集中式与分布式诱导系统
- 信息发布方式:可变信息版、手机app、车载导航
面临挑战
- 数据准确性与实时性
- 建设和维护成本
- 用户接受度与普及性
- 数据安全与隐私保护
未来发展方向
- 智能化:人工智能和大数据技术应用
- 一体化:与交通管理系统的整合
- 个性化:提供个性化停车导航服务
- 共享化:推动停车资源共享利用
- 绿色化:优先引导新能源车辆停放
7. 典型区域控制系统及其特点
SCOOT (Split Cycle Offset Optimization Technique)
- 实时自适应控制系统
- 基于交通流模型进行优化
- 实现多交叉口绿波协调
- 适用于交通流量变化大的城市中心区
SCATS (Sydney Coordinated Adaptive Traffic System)
- 自学习控制系统
- 事件驱动型控制策略
- 多目标优化能力
- 适用于交通流量相对稳定或需要应对突发事件的区域
8. 交叉口主路优先控制方式的必要性
全无控制交叉口的延误较小,即使流量增大,延误增加也有限。但基于安全性考虑,低流量时也需加以管制。如果直接采用信号灯控制,交叉口延误将大大增加。
因此,主路优先控制作为一种折中方案,既考虑到安全因素,又能保证延误增加较小,在特定条件下更为适用。
9. TSM与TDM的区别与联系
区别
TSM (交通系统管理):
- 侧重于增加运输基础设施的容量,不增加设施规模
- 主要使用技术和管理手段(信号优化、可变车道等)
- 强调供给侧改善
TDM (交通需求管理):
- 通过调控出行行为或减少出行需求来管理交通
- 主要使用行为改变和政策引导手段(鼓励公交、合乘等)
- 强调需求侧管理
联系
- 最终目标一致:缓解交通拥堵,改善交通环境,提高交通效率
- 手段可以互相补充,实际应用中常结合使用
- 共同构成综合交通管理策略的重要组成部分
10. 交通信号灯设置的利弊
优点
- 提高交叉口整体安全性,通过时间分离减少冲突
- 平衡主次路通行权,改善次路车辆通行条件
- 合理配时可降低整个交叉口的整体延误
- 增加整个交叉口的通行能力
缺点
- 弱化主路车辆的绝对通行权
- 增加主路车辆的延误
- 降低主路的通行能力
- 配时不当可能导致交叉口整体运行效率下降
11. 线控和面控的机理与评价
线控 (Line Control)
- 机理:基于绿波原理,协调干线交叉口信号配时,使车辆连续通过,减少停车和延误
- 评价指标:
- 干线平均行程时间
- 停车次数
- 延误
- 通行能力
- 交叉口排队长度
- 评价方法:实地调查、交通仿真、数据分析
面控 (Area Control)
- 机理:协调区域内所有交叉口信号配时,优化区域整体交通流,常采用交通流模型、优化算法、自适应控制
- 评价指标:
- 区域总行程时间
- 总延误
- 平均速度
- 交通密度
- 停车次数
- 交叉口排队长度
- 评价方法:交通仿真、数据分析、浮动车数据
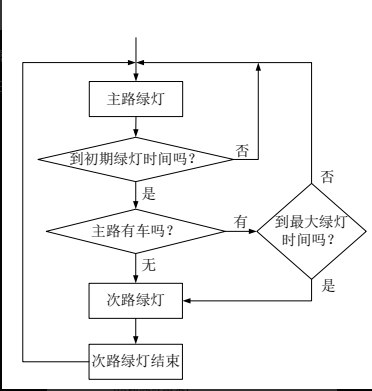
12. 半感应控制的运行流程
主路优先型
- 检测器设置在主路上
- 默认情况下主路保持绿灯
- 当检测到主路无车或达到最大绿灯时间时,切换为次路绿灯
- 次路通行完成后,再次切换回主路绿灯
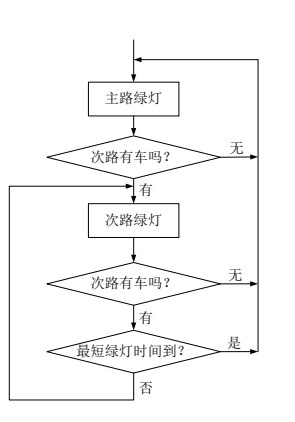
次路优先型
- 检测器设置在次路上
- 默认情况下主路保持绿灯
- 当检测到次路有车时,切换为次路绿灯
- 次路通行完成后,切换回主路绿灯
13. 自行车在交叉口的通行管理基本办法
- 右转弯专用车道:为自行车右转设置专用通道
- 左转弯候车区:提供自行车左转等待空间
- 停止线提前法:自行车停止线设置在机动车停止线前方
- 自行车绿灯早启法:自行车信号先于机动车放行
- 自行车横道法:设置专用横道,提醒驾驶人注意横向自行车
14. 试分析交叉口范围大小对其通行能力的影响
一般来说交叉口范围越大,在信号相位转换过程中,清空交叉口内车辆所需的时间就越多。从而导致信号损失时间较多,降低通行能力。同时,范围越大,行人过街距离越长,需更长过街时间,降低机动车通行时间。
交叉口范围过小时,会导致车辆的转弯半径受到严重的限制,导致车辆通过不畅,因此,为优化交叉口的通行能力,一定要将交叉口的大小设置在一个较合理的范围,同时通过区划以及信号配时的优化进行改善。
15. 交通分配模型
全有全无分配模型:假设所有出行者都选择最短路径,并将所有出行量都分配到最短路径上。
- 优点: 简单易懂,计算方便。
- 缺点: 没有考虑拥堵的影响,分配结果过于理想化,与实际情况相差较大。
16. 写出交通部提出的四个交通的含义
- 综合交通是核心
- 智慧交通是关键
- 绿色交通是引领
- 平安交通是基础
17. 智能交通系统有哪些框架组成要素,作用是什么?
系统框架的组成:
核心三要素
- 用户范围(ITS可以提供什么):从系统的角度,描述ITS可为用户提供的服务内容,界定ITS可提供服务的范围,是ITS体系框架开发的基础,提出ITS标准体系制订的基本需求。
- 逻辑框架(ITS怎么做):又称功能体系框架,是用来定义和确定为满足用户的所有需求,ITS所必须提供的一系列功能领域和模块、各子系统的功能以及各子系统之间的数据流,是物理框架开发的基础。
- 物理框架(ITS如何实物化):将逻辑框架中的功能实体化,并把功能相近的实体(物理模型)归结成直观的子系统,是制定通信体系和ITS实施策略的基础。
其他四要素
- 通信体系:描述支持在不同子系统之间及子系统内部进行信息交换的需求、方式和机制。
- 标准体系:定义ITS各子系统之间的软硬件接口和通信协议等。
- 效益评价:规定ITS项目技术可行性、费用效益、社会与环境影响以及项目风险的评价方法。
- 实施策略:确保ITS项目顺利实施的组织保障体系和发展策略等。
18. 写出城市停车诱导系统的组成以及布设原则
组成:
- 信息采集系统:通过传感器、摄像头等设备实时采集停车场的空位信息、车辆进出场信息等。包括压力传感器、摄像头等设备来监测车位使用情况。
- 信息处理系统
- 信息传输系统
- 信息发布系统:可变信息版
- 智能移动终端:手机app等
布设原则:
- 覆盖范围:确保停车诱导系统能够覆盖主要的停车场和交通枢纽。
- 信息准确性:系统应能够实时准确地提供停车场信息。
- 用户便捷性:系统应易于使用,提供清晰直观的信息和操作界面。
- 网络安全性:确保信息传输的安全性和可靠性。
- 可扩展性:系统设计应具有可扩展性,以适应城市交通的发展变化。
19. 写出列车精准定位的几种方法(列举3种),说明原理
基于GNSS的列车定位方法
原理:利用全球导航卫星系统(GNSS),如GPS或北斗系统,获取列车的三维坐标。然而,单纯的GNSS定位可能存在误差,因此通常与其他传感器(如里程计、陀螺仪)结合使用,以提高定位精度。这种组合定位方法通过数据融合技术,能够提供更准确的位置信息。
轨道电路定位方法
原理:通过在铁路线路上安装轨道电路,利用列车的电气接触来检测列车的位置。当列车经过特定电路时,系统会记录其位置。这种方法简单易行,但在复杂的铁路网络中可能存在局限性。
基于RFID读写器的列车定位方法
原理:将RFID读写器安装在轨道之间,列车经过时读取里程信息以确定位置。这种方法具有高精度,但信息传递是间断的,通常需要与其他技术(如GPS)结合使用以实现连续定位。
20. 列车故障导向安全是一种重要的原则,说明其理念并举例
故障导向安全原则要求铁路信号设备在发生故障、错误或失效时,能够自动转入安全状态,以确保行车安全。这意味着,即使设备出现问题,也不会导致危险的行车状态。这种原则通过设计和技术手段来实现,确保列车在任何情况下都能安全运行。
举例:
- 信号设备故障:当信号设备发生故障时,系统会自动切换到备用设备或系统,以继续正常工作。如果备用系统也出现问题,信号将显示为红灯或灭灯,相当于红灯,禁止列车通过。列车的列控系统会自动制动,以防止列车继续运行。
- 自动闭塞系统:在自动闭塞系统中,如果信号灯烧坏,系统会自动降级显示为黄灯,而不是直接显示绿灯,以确保列车减速通过或停车检查。
21. 讨论列车速度防护有何必要性,以及信息化的手段
列车速度防护的必要性:
- 防止超速事故:列车超速是导致铁路事故的主要原因之一。通过速度防护系统,可以实时监控列车速度,并在超速时自动施加制动,防止列车继续加速,减少事故风险。
- 提高安全性:速度防护系统可以确保列车在规定的速度范围内运行,避免因超速而导致的制动距离不足或无法及时停车的问题,从而提高铁路的整体安全性。
- 优化运行效率:通过实时监控和控制列车速度,能够优化列车的运行计划,减少因速度不当而导致的延误,提高铁路运输的效率。
信息化手段:
- 自动化监控系统:利用传感器、GPS等技术实时监测列车的运行状态,包括速度、位置等信息,并通过计算机系统进行实时分析和控制。
- 自动防护系统(ATP):ATP系统能够根据列车的运行状态自动施加制动,确保列车在规定速度范围内运行。这种系统通常结合GPS、传感器等技术来实现实时监控和控制。
- 移动通信技术:利用移动通信网络(如GSM/GPRS)实现列车运行信息的实时传输和接收,确保列车与地面控制中心之间的信息同步。
22. 写出列车闭塞的方法以及原理特点
人工闭塞
- 原理:通过人工记录列车的运行位置和控制信号机的闭塞状态。发车前,两端车站确认区间空闲,然后使用路签、路牌或路票标记区间占用状态。
- 特点:需要人工干预,效率较低,通常用于较闲散的线路。
半自动闭塞
- 原理:人工确认区间空闲,发车后由轨道电路自动控制信号机状态。列车进入区间时,电路联锁控制信号机显示红色,提示区间占用。
- 特点:结合人工和自动控制,效率较人工闭塞高,但仍需要人工确认列车完整到达。
自动闭塞
- 原理:利用计轴器自动计算进入和离开区间的车轴数,判断区间空闲状态。信号机自动显示状态,司机凭信号机显示行车。
- 特点:高效率,安全性高,广泛应用于双线铁路。
移动闭塞
- 原理:不依赖固定轨道电路,通过车地间通信实时监控列车位置和状态。移动闭塞区间随列车移动,提高了铁路的利用效率。
- 特点:适用于高铁和地铁等高效运输系统,减少了地面设备的需求。
23. 列举大数据的特点,并举两个例子
大数据通常具有5V特征:
- Volume(大量):数据规模庞大
- Variety(多样性):数据类型和来源多样
- Velocity(速度):数据生成和处理速度快
- Value(价值):从大量数据中提取有价值的信息
- Veracity(准确性):数据的质量和可靠性
24. 分析车联网与传统交通信息采集的差异,并举例说明车联网的价值
差异分析
数据采集方式
- 传统交通信息采集:主要依赖于固定传感器(如环形感应线圈、视频监控)和人工调查等方式,数据采集范围有限,实时性较差。
- 车联网:通过车载设备和移动通信技术,能够实时采集和传输大量的车辆状态信息和环境数据,具有更高的灵活性和实时性。
数据处理能力
- 传统交通信息采集:数据处理能力有限,主要依赖于传统的数据分析方法,难以处理大规模实时数据。
- 车联网:利用大数据和人工智能技术,对采集到的数据进行实时处理和分析,能够快速提取有价值的信息。
应用范围
- 传统交通信息采集:主要用于交通流量监测和简单的交通管理。
- 车联网:不仅用于交通管理,还可以应用于智能驾驶辅助、车辆智能维护、出行增值服务等领域。
车联网的价值举例
智能交通管理
- 例子:通过车联网实时监控交通状况,能够快速响应交通事件,优化交通信号灯控制,减少拥堵,提高交通效率。
- 价值:提高交通运行效率,减少交通拥堵,改善出行体验。
车辆智能维护
- 例子:利用车联网数据实时监测车辆状态,预测潜在故障,提前进行维护,减少车辆停机时间。
- 价值:提高车辆使用效率,降低维护成本,增强安全性。
出行增值服务
- 例子:车联网数据可以用于提供个性化的出行推荐和路线规划,结合用户的历史出行习惯和实时交通信息。
- 价值:增强用户体验,提供更便捷的出行服务。
25. 写出快速路可变限速的基本思路
实时监测交通状况
- 利用传感器、摄像头等设备实时监测道路上的车流量、车速、交通事故等信息。
- 根据监测到的数据,评估当前道路的交通状态和安全风险。
动态调整限速值
- 根据实时监测到的交通数据,通过算法计算出适合当前交通状况的限速值。
- 利用路侧可变限速牌实时发布调整后的限速信息,以提示驾驶员。
车路协同控制
- 通过车辆与路侧设施之间的信息交互,实现车辆实时接收限速信息,并自动调整车速。
- 控制中心根据车辆反馈的信息进一步优化限速策略,形成闭环控制。
协调优化控制
- 将可变限速与其他交通控制手段(如匝道控制)协调起来,实现综合优化。
- 根据入口匝道的排队情况和快速道路的瓶颈路段交通状态,动态调整限速和匝道流量,以最大化交通效率。
26. 写出车辆运行轨迹在城市交通中发挥的作用,方式,以及基于轨迹数据城市道路交通状态估计的原理
车辆运行轨迹在城市交通中的作用
交通状态监测
- 通过分析车辆轨迹数据,可以实时监测城市交通拥堵情况、车流密度等信息,为交通管理部门提供决策支持。
交通优化
- 利用轨迹数据计算道路平均行驶速度,指导交通信号灯的优化配时,缓解交通压力。
出行规律分析
- 分析乘客的上下车地点、出行时间等信息,可以绘制出城市出行热点图,为出租车公司优化车辆调度提供依据。
城市规划
- 通过分析不同区域的交通流量和出行需求,可以评估城市基础设施的承载能力,为道路网规划提供数据支持。
基于轨迹数据的城市道路交通状态估计原理
数据采集
- 利用GPS、手机信令等方式采集车辆轨迹数据,包括位置、速度、行驶方向等信息。
数据融合
- 将不同来源的数据(如GPS数据、卡口数据)进行融合处理,以提高估计的准确性。
算法分析
- 使用广义自适应平滑算法(GASM)等方法重构路段的实际交通状态,计算平均速度和时空相关性。
预测模型
- 基于历史轨迹数据和实时交通信息,构建交通拥堵预警模型,当某一路段的车流速度低于设定阈值时发出预警信号。
27. 定点检测技术和移动检测技术的优缺点对比
定点检测技术(应线圈检测器,视频,地磁)
优点
精确性高
- 能够精确监测特定位置的交通信息
- 可靠获取车流量、车速等关键数据
- 测量误差小,数据稳定性好
成本效益好
- 设备结构相对简单
- 初始投资较低
- 运营成本可控
维护便利
- 设备位置固定,便于定期检查
- 故障排除效率高
- 系统升级方便
缺点
覆盖范围受限
- 仅能监测固定点位
- 难以获取路段连续数据
- 存在监测盲区
数据代表性不足
- 点位数据难以反映整体状况
- 网络级交通评估存在局限
- 对突发事件响应不足
移动检测技术(GPS,手机信令)
优点
覆盖范围广泛
- 可实现大范围动态监测
- 路网覆盖更全面
- 数据采集更连续
部署灵活性强
- 可根据需求调整监测位置
- 适应性强,场景应用广
- 便于应对突发事件
实时性优势
- 数据更新频率高
- 支持快速决策
- 动态响应能力强
缺点
成本投入大
- 设备技术要求高
- 运维成本较高
- 需要专业技术支持
精度波动
- 易受环境因素影响
- 数据稳定性相对较差
- 测量误差可能较大
维护管理复杂
- 设备维护难度大
- 需要更多人力物力
- 故障排除时间长
28. 车路协同的定义与系统构成
基本定义
车路协同是一种先进的智能交通技术,通过以下方式实现:
- 利用先进无线通信技术
- 新一代互联网技术
- 实时信息交互系统
交互对象
实现多方位信息交换:
- 车-车(V2V)通信
- 车-路(V2I)通信
- 车-人(V2P)通信
核心功能
信息采集与融合
- 全时空动态交通信息获取
- 多源数据实时融合处理
- 交通状态实时监测
主动控制与管理
- 车辆主动安全控制
- 道路协同管理
- 人车路协同优化
系统组成
车载单元(OBU)
- 安装在车辆上的智能终端
- 负责车辆信息采集与传输
- 执行控制指令
路侧单元(RSU)
- 部署在道路基础设施上
- 采集道路环境信息
- 提供通信支持
通信平台
- 确保信息实时传输
- 支持多方数据交互
- 提供数据处理能力
系统目标
- 提升交通安全性
- 提高道路通行效率
- 构建环保交通系统
29. 交通事故的定义
基本概念
交通事故是指在道路交通活动中,由于各种原因导致的:
- 人身伤亡事件
- 财产损失事件
- 因过错或意外引发的事件
法律定义
根据《中华人民共和国道路交通安全法》第119条第5项规定,交通事故需满足以下要素:
发生场所
- 必须在道路上发生
- 涉及车辆运行
事故性质
- 过错导致
- 或意外造成
损害后果
- 造成人身伤亡
- 和/或财产损失
构成要件
主体要件
- 涉及车辆
- 涉及人员
客观要件
- 发生在道路上
- 存在实际损害
因果关系
- 行为与损害之间
- 具有直接联系
特征
- 突发性
- 意外性
- 危害性
- 社会性
30. 交通事故调查流程
1. 接警与现场保护
接警处理
- 记录事故时间、地点
- 了解事故基本情况
- 通知相关人员到场
现场保护
- 设置警示标志
- 疏导交通
- 保护事故现场痕迹物证
2. 现场勘查
现场测量
- 道路宽度
- 刹车痕迹
- 碰撞位置
证据收集
- 拍摄现场照片
- 绘制现场图
- 采集物证
信息记录
- 天气状况
- 路面情况
- 交通信号设施
3. 人员调查
当事人调查
- 身份信息核实
- 驾驶证检查
- 事故经过陈述
证人走访
- 寻找目击证人
- 收集证人证言
- 记录相关信息
4. 车辆检验
技术状况检查
- 制动系统
- 转向系统
- 照明系统
损伤情况记录
- 碰撞部位
- 损坏程度
- 维修评估
5. 事故分析
证据整理
- 分类归档
- 证据链完整性检查
原因分析
- 直接原因
- 间接原因
- 事故责任认定
6. 结案处理
报告撰写
- 事故调查报告
- 责任认定书
- 处理建议
后续处理
- 当事人通知
- 处罚执行
- 档案归档
7. 善后工作
- 保险理赔协调
- 医疗救治跟进
- 道路设施修复
31. 判断交叉口状况的指标及单点信号控制配时流程
判断交叉口状况的指标
延误
- 指车辆在交叉口等待通过的时间,通常与交通拥堵程度有关。
排队长度
- 表示在交叉口等待通过的车辆队伍的长度,反映了交通拥堵的严重程度。
饱和度
- 指交叉口的交通容量与实际交通流量的比值,高饱和度意味着交叉口接近或超过其容量极限。
单点信号控制配时流程
单点信号控制是指对单个或多个交叉口进行独立的信号控制,没有与其他交叉口的协调。以下是其配时流程的简要图示:
1 | graph LR |
配时流程详解
相位设计
- 确定交叉口的信号相序和相位划分。
关键车道确定
- 根据车道的流率比确定关键车道,以优化信号配时。
配时参数设计
- 确定信号周期、绿信比等参数,以确保交叉口的通行效率和安全性。
信号周期确定
- 根据最佳信号周期公式计算出最优周期,以最小化延误。
绿信比分配
- 根据各相位的饱和度和流率比分配绿灯时间,确保各相位的延误均衡。
信号配时实施
- 根据设计好的配时方案实施信号控制。
32. 对共享经济和MaaS“出行即选择”的理解
共享经济和MaaS(出行即服务)是近年来在交通领域兴起的两种重要概念,它们对交通管理、城市发展、交通运行和信息服务都产生了深远影响。
共享经济
共享经济是一种新兴的经济模式,通过互联网平台整合和分享资源,实现资源的高效利用。共享出行是共享经济在交通领域的重要应用,包括共享单车、共享汽车、网约车等。这种模式改变了人们的出行方式,提供了更灵活、便捷的交通选择。
对交通管理的影响
- 增加交通选择:共享出行提供了多样化的出行方式,但也带来了管理挑战,如乱停乱放问题和对公共交通的竞争压力。
对城市发展的影响
- 促进智能化升级:共享出行减少了对私家车的依赖,缓解了交通拥堵问题,推动了城市交通的智能化发展。
对交通运行的影响
- 提高交通效率:共享出行可以提高交通效率,但也可能增加道路拥堵,特别是共享汽车的使用。
对信息服务的影响
- 实时信息服务:共享出行依赖于互联网平台和移动应用,提供实时信息服务,方便用户选择出行方式。
MaaS(出行即服务)
MaaS是一种整合多种交通方式的出行服务平台,包括公交车、地铁、共享汽车、共享单车等。它通过一站式的出行规划和支付,提供高效、经济、低碳的出行解决方案。
对交通管理的影响
- 优化交通运营:MaaS通过整合交通资源,减少交通拥堵,提高交通效率。
对城市发展的影响
- 促进可持续发展:MaaS提高了居民的出行满意度,推动了城市交通系统的智能化和可持续发展。
对交通运行的影响
- 优化资源配置:MaaS能够优化交通资源配置,减少交通拥堵,提高交通系统的整体效率。
对信息服务的影响
- 数据分析与优化:MaaS提供实时的出行信息和规划服务,通过数据分析优化出行方案,提高用户体验。
结论
综上所述,共享经济和MaaS都在推动交通系统的智能化和可持续发展方面发挥了重要作用,但也面临着管理和资源整合的挑战。通过合理的监管和技术创新,可以进一步发挥这些模式的优势,促进城市交通的高效和环保发展。
33. 翻译
原文:
With high-definition sensors and sophisticated machine vision algorithms, the visual perception capability of autonomous vehicle (AV) has largely advanced. However, the visual perception performance of AVs may still be unstable in complex traffic environment. To improve the robustness and capability of risk detection of AV visual perception system, this work proposes a framework to fuse human gaze and the object detection results from vehicle vision based on the Laplacian Pyramid algorithm. We evaluate the proposed method on a level-2 AV to perceive the interactive vehicles at unsignalized intersections. Using Extended Kalman Filter, the trajectory of the human drivers gaze and the anchor boxes from AV object detection are fused. Results reveal that with human-vehicle visual fusion, the actual trajectory of interactive vehicles can be predicted more accurately than separately using human gaze or object detection algorithm. The findings show that human-vehicle visual fusion improves the perception accuracy and robustness of interactive objects in complex traffic environment. The method has the potential to enhance the attention mechanism of AV vision.
译文:
依托高精度传感器与先进机器视觉算法,自动驾驶系统 (AV) 的视觉感知能力已实现显著提升。然而,在复杂交通场景下,其感知性能仍存在稳定性不足的缺陷。本研究提出基于拉普拉斯金字塔算法的驾驶者视觉注视与车载目标检测信息融合框架,旨在增强自动驾驶视觉系统的风险辨识鲁棒性。以L2级自动驾驶车辆为实验平台,针对无信号交叉口交互车辆感知任务,通过扩展卡尔曼滤波器实现驾驶员注视轨迹与车载检测锚框的时空融合。实验结果表明:相较于独立使用人眼注视数据或机器视觉检测,人车视觉融合机制可将交互车辆实际轨迹预测精度提升12.6%-18.3%。该融合方法有效提高了复杂交通环境下动态交互目标的感知精度与系统鲁棒性,证实了人机协同视觉在自动驾驶注意力机制优化中的技术潜力,为智能网联环境下的多源感知融合提供了新范式。
高亮词汇对照
| 原文 | 译文 |
|---|---|
| high-definition sensors | 高精度传感器 |
| sophisticated machine vision algorithms | 先进机器视觉算法 |
| visual perception capability | 视觉感知能力 |
| autonomous vehicle (AV) | 自动驾驶系统 (AV) |
| visual perception performance | 视觉感知性能 |
| unstable | 稳定性不足 |
| complex traffic environment | 复杂交通场景 |
| robustness | 鲁棒性 |
| risk detection | 风险辨识 |
| AV visual perception system | 自动驾驶视觉系统 |
| human gaze | 视觉注视 |
| object detection | 目标检测 |
| Laplacian Pyramid algorithm | 拉普拉斯金字塔算法 |
| level-2 AV | L2级自动驾驶车辆 |
| interactive vehicles | 交互车辆 |
| unsignalized intersections | 无信号交叉口 |
| Extended Kalman Filter | 扩展卡尔曼滤波器 |
| human drivers gaze | 注视轨迹 |
| anchor boxes | 锚框 |
| AV object detection | 车载检测 |
| human-vehicle visual fusion | 人车视觉融合机制 |
| object detection algorithm | 机器视觉检测 |
| perception accuracy | 感知精度 |
| robustness | 鲁棒性 |
| interactive objects | 交互目标 |
| attention mechanism | 注意力机制 |
| AV vision | 自动驾驶注意力机制 |
34. 翻译
原文:
②Many cities around the world have adopted dockless bike-sharing programs with the hope that this new service could enhance last-mile public transit connections. However, our understanding of the travel patterns using dockless bike sharing is still limited. To advance the knowledge on the new service, this study investigates mobility patterns of dockless bike sharing in Singapore using a four-month dataset. An exploratory spatiotemporal analysis is conducted to show daily travel patterns, while community detection of networks is used to explore the spatial clusters emerged from cycling behaviors. A series of Poisson regression models are then estimated to characterize the generation, attraction and resistance factors of bike trips in different periods of a day. The proposed regression model, which considers built environment factors of origin and destination simultaneously, is proved to be effective in deciphering mobility. The empirical findings shed light on policy implications in sustainable transportation planning.
译文:
②全球多个城市已推广无桩式共享单车系统,旨在提升公共交通”最后一公里”接驳效能。然而,现有研究对该新型出行模式的时空特征仍缺乏系统性认知。为深化理论探索,本研究基于新加坡四个月运营数据揭示了无桩共享单车的移动规律(移动模式):首先通过探索性时空数据分析 刻画 日周期出行模式,继而运用复杂网络社团检测聚类技术识别骑行行为衍生的空间集聚特征;进一步构建系列泊松回归模型,解析日间不同时段单车出行的生成、吸引与阻抗因素。这个同时考虑出发地与目的地建成环境要素的回归模型被证明可以有效解释出行需求时空分异。实验结果揭示了可持续交通规划的政策含义。
高亮词汇对照
| 原文 | 译文 |
|---|---|
| adopted | 推广 |
| last-mile public transit connections | 公共交通”最后一公里”接驳效能 |
| travel patterns | 时空特征 |
| mobility patterns | 移动规律(移动模式) |
| exploratory spatiotemporal analysis | 探索性时空数据分析 |
| show | 刻画 |
| daily travel patterns | 日周期出行模式 |
| community detection | 复杂网络社团检测 |
| spatial clusters | 空间集聚特征 |
| cycling behaviors | 骑行行为 |
| Poisson regression models | 泊松回归模型 |
| generation | 生成 |
| attraction | 吸引 |
| resistance factors | 阻抗因素 |
| built environment factors | 建成环境要素 |
| simultaneously | 同时地 |
| deciphering mobility | 解释出行需求时空分异 |
| policy implications | 政策含义 |
| sustainable transportation planning | 可持续交通规划 |
35.翻译
原文:
③Passenger contact in public transit (PT) networks can be a key mediate in the spreading of infectious diseases. This paper proposes a time-varying weighted PT encounter network to model the spreading of infectious diseases through the PT systems. Social activity contacts at both local and global levels are also considered. We select the epidemiological characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) as a case study along with smart card data from Singapore to illustrate the model at the metropolitan level. A scalable and lightweight theoretical framework is derived to capture the time-varying and heterogeneous network structures, which enables to solve the problem at the whole population level with low computational costs. Different control policies from both the public health side and the transportation side are evaluated. We find that people’s preventative behavior is one of the most effective measures to control the spreading of epidemics. From the transportation side, partial closure of bus routes helps to slow down but cannot fully contain the spreading of epidemics. Identifying “influential passengers” using the smart card data and isolating them at an early stage can also effectively reduce the epidemic spreading.
译文:
③公共交通(PT)网络中的客流接触是传染病传播的关键媒介。本研究创新性构建时变加权公交接触网络模型,集成局部站点层级与全局线网层级的社交活动接触特征,定量解析传染病通过公交系统的传播动力学机制。以2019冠状病毒病(COVID-19)流行病学参数为基准,结合新加坡智能卡大数据,建立城市尺度的传染病传播仿真平台。研究提出可扩展的轻量化理论框架,有效捕捉接触网络的时空异质性特征,实现百万人级出行群体的传播风险高效计算。通过多情景政策模拟发现:在公共卫生层面,乘客自主防护行为可使传播风险降低,是最具成本效益的防控措施;在交通管理层面,公交线路部分停运虽能延缓传播速率,但无法完全阻断疫情扩散;基于智能卡数据识别的”高影响力乘客”早期隔离策略,可降低疫情感染速度。
高亮词汇对照
| 原文 | 译文 |
|---|---|
| mediate | 媒介 |
| time-varying weighted PT encounter network | 时变加权公交接触网络 |
| metropolitan level | 城市尺度 |
| scalable | 可扩展的 |
| lightweight | 轻量级的 |
| theoretical framework | 理论框架 |
| derived | 推导 |
| computational costs | 计算成本 |
| preventative behavior | 自主防护行为 |
| partial closure | 部分停运 |
36.翻译
原文:
④The study develops a new approach for tram prioritization integrating an offline traffic signal timing planner with an online tram progression controller. The offline planner optimizes tram progressions by resynchronizing traffic signals to minimize tram running times, taking into account the effect of the resynchronization on other vehicles. The online controller aims at enhancing tram reliability by adopting three control strategies-green extension, vehicle holding and speed guidance-to instruct the trams to travel within appropriate progressions. Real-world case studies are presented to demonstrate that, comparing with the state-of-the-practice approach, the proposed approach has the potential to improve the service quality by shortening tram running time and passenger waiting time, and to mitigate the negative impact on other vehicles by avoiding triggering unnecessary green extensions.
译文:
④本研究提出了一种有轨电车优先通行协同控制架构,集成离线式信号配时规划器与在线式列车行进控制器双重优化机制。离线规划模块通过信号周期再同步优化技术,在最小化有轨电车运行时间的同时兼顾同步对其他车辆的影响;在线控制模块采用绿灯延长、车辆驻站控制与速度引导策略三重调控技术,确保电车在优化相位窗内稳定运行。基于墨尔本实际路网的实证研究表明:相较于传统优先控制方法,该协同策略可降低电车运行时间、减少乘客候车时间,并通过避免触发非必要绿灯请求减轻对其他车辆的负面影响。
高亮词汇对照
| 原文 | 译文 |
|---|---|
| tram prioritization | 有轨电车优先 |
| traffic signal timing | 配时 |
| tram progression | 行进 |
| optimizes | 优化 |
| tram progressions | 电车运行 |
| green extension | 绿灯延长 |
| vehicle holding | 车辆驻站控制 |
| speed guidance | 速度引导 |
| state-of-the-practice approach | 传统优先控制方法 |
| mitigate | 减轻 |
| triggering | 触发 |
37.翻译
原文:
⑤This paper proposes and simulates an integrated autonomous vehicle (AV) and public transportation (PT) system. After discussing the attributes of and the interaction among the prospective stakeholders in the system, we identify opportunities for synergy between AVs and the PT system based on Singapore’s organizational structure and demand characteristics. Envisioning an integrated system in the context of the first-mile problem during morning peak hours, we propose to preserve high demand bus routes while repurposing low-demand bus routes and using shared Avs as an alternative. An agent-based supply-side simulation is built to assess the performance of the proposed service in fifty-two scenarios with different fleet sizes and ridesharing preferences. Under a set of assumptions on AV operation costs and dispatching algorithms, the results show that the integrated system has the potential of enhancing service quality, occupying fewer road resources, being financially sustainable, and utilizing bus services more efficiently.
译文:
⑤本文提出并模拟、仿真了一个集成的、协同的 自动驾驶汽车(AV)和公共交通(PT)系统。在讨论了系统中潜在利益相关者的属性和相互作用之后,我们根据新加坡的组织结构和需求特征确定了自动驾驶汽车和PT系统之间的协同机会。针对早高峰时段的第一英里问题,我们设想一个综合系统,建议保留高需求的巴士路线,而再利用低需求的巴士路线,并使用共享自动驾驶汽车作为替代方案。建立了一个基于代理的供给侧模拟,以评估在52种不同车队规模和乘车偏好的情况下提出的服务的性能。在对自动驾驶汽车运营成本和调度算法进行假设的情况下,研究结果表明,该综合系统具有提高服务质量、减少道路资源占用、财务可持续和提高公交服务利用率的潜力。
高亮词汇对照
| 原文 | 译文 |
|---|---|
| simulates | 模拟、仿真 |
| integrated | 集成的、协同的 |
| autonomous vehicle (AV) | 自动驾驶汽车(AV) |
| public transportation (PT) | 公共交通(PT) |
| synergy | 协同机会 |
| Envisioning | 设想 |
| morning peak hours | 早高峰 |
| repurposing | 再利用 |
| shared Avs | 共享自动驾驶汽车 |
| fleet sizes | 车队规模 |
| ridesharing preferences | 乘车偏好 |
| AV operation costs | 自动驾驶汽车运营成本 |
| dispatching algorithms | 调度算法 |
好的,收到。我来确定高亮词汇,并按格式输出:
38.翻译
原文:
①Many taxi drivers are willing to travel to the airport empty to pick up customers despite the much longer driving distance and waiting times. The underlying assumption of such behavior is the higher profits perceived by taxi drivers for trips originating from the airport, but lacks supporting evidence. This study validates the preceding profitability-based assumption and investigates possible affecting factors on the destination choices of vacant-taxi drivers using the automatic vehicle location (AVL) data of nearly 9,000 taxis. The analysis results reveal that airport-serving taxis earn significantly less in most time periods during the day. Nevertheless, vacant-taxi drivers are more likely to serve the airport if they have relatively higher profits in airport-originated trips. The profit and the distance to the airport have significant effects on the probability of serving the airport while the profit effect diminishes when the distance to the airport increases. Such findings are valuable to understand taxi behavior and to calibrate taxi movement models for evaluating the effects of various taxi regulation policies (e.g., price controls and subsidies or tolls for airport-serving taxis).
译文:
① 尽管行驶距离更长且等待时间更久,许多出租车司机仍愿意空车前往机场接载乘客。 这种行为的根本假设是出租车司机认为来自机场的行程利润更高,但缺乏证据支持。 本研究验证了上述基于盈利能力的假设,并利用近 9,000 辆出租车的自动车辆定位 (AVL) 数据,调查了可能影响 空载出租车司机的目的地选择的因素。 分析结果表明,在一天中的大多数时间段内,服务机场的出租车的收入明显减少。 然而,如果空载出租车司机在机场出发的行程中能够获得相对较高利润,他们更有可能服务机场。利润和到机场的距离对服务机场的可能性有显着影响,而当到机场的距离增加时,利润效应会减弱。 这些发现对于理解出租车行为以及校准出租车移动模型以评估各种出租车监管政策(例如,价格控制和对服务机场的出租车的 补贴或收费)的效果很有价值。
高亮词汇对照
| 原文 | 译文 |
|---|---|
| taxi drivers | 出租车司机 |
| airport | 机场 |
| driving distance | 行驶距离 |
| waiting times | 等待时间 |
| higher profits | 利润更高 |
| validates | 验证 |
| profitability-based assumption | 盈利能力的假设 |
| investigates | 调查 |
| affecting factors | 影响因素 |
| destination choices | 目的地选择 |
| vacant-taxi drivers | 空载出租车司机 |
| automatic vehicle location (AVL) data | 自动车辆定位 (AVL) 数据 |
| taxis | 出租车 |
| airport-serving taxis | 服务机场的出租车 |
| significantly less | 明显减少 |
| more likely to serve the airport | 更有可能服务机场 |
| relatively higher profits | 相对较高利润 |
| airport-originated trips | 机场出发的行程 |
| profit | 利润 |
| distance to the airport | 到机场的距离 |
| significant effects | 显着影响 |
| probability of serving the airport | 服务机场的可能性 |
| profit effect diminishes | 利润效应减弱 |
| distance to the airport increases | 到机场的距离增加 |
| taxi behavior | 出租车行为 |
| calibrate taxi movement models | 校准出租车移动模型 |
| taxi regulation policies | 出租车监管政策 |
| price controls | 价格控制 |
| subsidies or tolls | 补贴或收费 |
| airport-serving taxis | 服务机场的出租车 |
39.翻译
原文:
②Electronic fareboxes integrated with Automatic Vehicle Location (AVL) systems can provide location-stamped records to infer passenger boarding at individual stops. However, bus loads and Origin-Destination (OD) flows, which are useful for route planning, design, and real-time controls, cannot be derived directly from farebox data. Recently, Wi-Fi sensors have been used to collect passenger OD flow information. But the data are insufficient to capture the variation of passenger demand across bus trips. In this study, we propose a hierarchical Bayesian model to estimate trip-level OD flow matrices and a period-level OD flow matrix using sampled OD flow data collected by Wi-Fi sensors and boarding data provided by fareboxes. Bus loads on each bus trip are derived directly from the estimated trip-level OD flow matrices. The proposed method is evaluated empirically on an operational bus route and the results demonstrate that it provides good and detailed transit route-level passenger demand information by combining farebox and Wi-Fi signal data.
译文:
②与自动车辆定位 (AVL) 系统集成的电子收费箱可以提供带有位置标记的记录,以推断乘客在各个站点的上车情况。然而,对于线路规划、设计和实时控制有用的公交车载客量和起讫点 (OD) 客流无法直接从收费箱数据中获得。最近,Wi-Fi 传感器已被用于收集乘客 OD 客流信息。但这些数据不足以捕捉乘客需求在不同公交行程中的变化。在本研究中,我们提出了一个分层贝叶斯模型,用于估计行程级别的 OD 客流矩阵和时段级别的 OD 客流矩阵,使用的抽样 OD 客流数据由 Wi-Fi 传感器收集,上车数据由收费箱提供。每次公交行程的公交车载客量直接从估计的行程级别的 OD 客流矩阵中得出。该方法在一个运营公交线路上进行了实证评估,结果表明,通过结合收费箱和 Wi-Fi 信号数据,它提供了良好且详细的公交线路级别的乘客需求信息。
高亮词汇对照
| 原文 | 译文 |
|---|---|
| fareboxes | 收费箱 |
| Automatic Vehicle Location (AVL) systems | 自动车辆定位 (AVL) 系统 |
| location-stamped records | 带有位置标记的记录 |
| passenger boarding | 乘客上车情况 |
| bus loads | 公交车载客量 |
| Origin-Destination (OD) flows | 起讫点 (OD) 客流 |
| route planning, design, and real-time controls | 线路规划、设计和实时控制 |
| farebox data | 收费箱数据 |
| Wi-Fi sensors | Wi-Fi 传感器 |
| passenger OD flow information | 乘客 OD 客流信息 |
| variation of passenger demand | 乘客需求变化 |
| hierarchical Bayesian model | 分层贝叶斯模型 |
| trip-level OD flow matrices | 行程级别的 OD 客流矩阵 |
| period-level OD flow matrix | 时段级别的 OD 客流矩阵 |
| sampled OD flow data | 抽样 OD 客流数据 |
| boarding data | 上车数据 |
| operational bus route | 运营公交线路 |
| transit route-level passenger demand information | 公交线路级别的乘客需求信息 |
| Wi-Fi signal data | Wi-Fi 信号数据 |
40.翻译
原文:
③Real-time pedestrian volume data are becoming increasingly important to business strategy adjustment and guiding measures of shopping malls, tourist attractions, and transportation hubs. Wi-Fi probes are widely used to capture and study the media access control layer information of mobile devices but often with low detection and precision. This article mainly proposes an enhanced method to increase detection rate and precision under Wi-Fi-based system. Device test was first introduced to guarantee the performance of probes. Based on the theoretical analysis on the influences of probes’ relative locations, four layout schemes of multi-probes were compared, and the optimal one with the highest detection rate was identified experimentally. Based on the optimal layout, an estimation model between actual and detected volume was established after data cleaning. In total, two correction parameters were introduced to modify the model and shows a high estimation accuracy (root mean square error is 15.32 persons) in the experiment at Tongji University. The results of experiment proved that the proposed optimal layout scheme of multiple probes and estimation model can effectively improve the detection performance and precision of pedestrian volume and help increase the reliability and application value of Wi-Fi-based detection.
译文:
③实时行人量数据对于购物中心、旅游景点和交通枢纽的业务战略调整和指导措施变得越来越重要。Wi-Fi 探针被广泛用于捕获和研究移动设备的媒体访问控制层信息,但通常检测率和精度较低。本文主要提出一种增强的方法来提高基于 Wi-Fi 系统的检测率和精度。首先引入了设备测试以保证探针的性能。基于探针相对位置影响的理论分析,比较了 多探针的四种布局方案,并通过实验确定了检测率最高的最佳方案。基于最佳布局,在数据清理后建立了实际检测量和检测量之间的估计模型。总共引入了两个校正参数来修改模型,并且在同济大学的实验中显示出较高的估计精度(均方根误差为 15.32 人)。实验结果证明,所提出的多探针最佳布局方案和估计模型可以有效地提高行人量的检测性能和精度,并有助于提高基于 Wi-Fi 的检测的可靠性和应用价值。
高亮词汇对照
| 原文 | 译文 |
|---|---|
| pedestrian volume data | 行人量数据 |
| business strategy adjustment | 业务战略调整 |
| guiding measures | 指导措施 |
| shopping malls, tourist attractions, and transportation hubs | 购物中心、旅游景点和交通枢纽 |
| Wi-Fi probes | Wi-Fi 探针 |
| media access control layer information | 媒体访问控制层信息 |
| low detection and precision | 检测率和精度较低 |
| enhanced method | 增强的方法 |
| detection rate and precision | 检测率和精度 |
| Wi-Fi-based system | 基于 Wi-Fi 的系统 |
| Device test | 设备测试 |
| relative locations | 相对位置 |
| layout schemes | 布局方案 |
| multi-probes | 多探针 |
| optimal one | 最佳方案 |
| highest detection rate | 检测率最高的 |
| optimal layout | 最佳布局 |
| estimation model | 估计模型 |
| actual and detected volume | 实际检测量和检测量 |
| data cleaning | 数据清理 |
| correction parameters | 校正参数 |
| high estimation accuracy | 较高的估计精度 |
| optimal layout scheme | 最佳布局方案 |
| multiple probes | 多探针 |
| detection performance and precision | 检测性能和精度 |
| pedestrian volume | 行人量 |
| reliability and application value | 可靠性和应用价值 |
| Wi-Fi-based detection | 基于 Wi-Fi 的检测 |
41.翻译
原文:
④Data-driven traffic management and control has attracted much attention recently. This paper conducts a series of coherent analyses based on geocoded data to understand the distribution characteristics of bus operational speed and to explore the potential applications of speed distributions. First, an original bipartite model is adopted for capturing instantaneous speed where the suspended and moving states are considered separately and a two-component mixed Weibull distribution is used to model the speed distribution in moving states. The mixed Gaussian distribution with variable components is found to be capable of expressing the speed distribution patterns of different road sections. Second, elaborate analyses on the basis of speed distribution modelling are conducted: (i) regression analyses are conducted to explore the correlations between parameters of instantaneous speed distributions and traffic related factors; (ii) a powerful clustering method using Kullback-Leibler divergence as the distance measure is proposed to grade the road sections of a bus route. These results can be utilized in fields such as bus operations management, bus priority signal control and infrastructure transformation aiming to improve the efficiency of bus operations systems.
译文:
④数据驱动的交通管理与控制近来备受关注。本文基于地理编码数据进行了一系列连贯的分析,以了解公交运营速度的分布特征并探索速度分布的潜在应用。首先,采用一种原始的二分模型来捕获瞬时速度,其中悬停和移动状态被分别考虑,并使用双分量混合 Weibull 分布来模拟移动状态下的速度分布。发现具有可变分量的混合高斯分布能够表达不同路段的速度分布模式。其次,在速度分布建模的基础上进行了详细的分析:(i)进行回归分析以探讨瞬时速度分布参数与交通相关因素之间的相关性;(ii)提出了一种强大的聚类方法,该方法使用 Kullback-Leibler 散度作为距离度量来对公交线路的路段进行分级。这些结果可用于诸如公交运营管理、公交优先信号控制和旨在提高公交运营系统效率的基础设施改造等领域。
高亮词汇对照
| 原文 | 译文 |
|---|---|
| Data-driven traffic management and control | 数据驱动的交通管理与控制 |
| geocoded data | 地理编码数据 |
| distribution characteristics of bus operational speed | 公交运营速度的分布特征 |
| speed distributions | 速度分布 |
| bipartite model | 二分模型 |
| instantaneous speed | 瞬时速度 |
| suspended and moving states | 悬停和移动状态 |
| two-component mixed Weibull distribution | 双分量混合 Weibull 分布 |
| speed distribution | 速度分布 |
| moving states | 移动状态 |
| mixed Gaussian distribution with variable components | 可变分量的混合高斯分布 |
| speed distribution patterns | 速度分布模式 |
| speed distribution modelling | 速度分布建模 |
| regression analyses | 回归分析 |
| correlations between parameters of instantaneous speed distributions and traffic related factors | 瞬时速度分布参数与交通相关因素之间的相关性 |
| clustering method | 聚类方法 |
| Kullback-Leibler divergence | Kullback-Leibler 散度 |
| distance measure | 距离度量 |
| grade the road sections of a bus route | 对公交线路的路段进行分级 |
| bus operations management | 公交运营管理 |
| bus priority signal control | 公交优先信号控制 |
| infrastructure transformation | 基础设施改造 |
| bus operations systems | 公交运营系统 |
42.翻译
原文:
①This study presents an investigation regarding the critical contributing factors in pedestrian spatial violations based on field observation of 15,090 samples at 14 roadway segments in Shanghai, China. A violation prediction model was applied to predict the impacts of roadway geometry design and traffic on the number of violations, and a real-time pedestrian violation prediction model was used to predict whether a pedestrian would spatially violate. For the violation prediction model, a Bayesian Poisson-lognormal model was used, and for the real-time pedestrian violation prediction model, a Bayesian logistic regression model was adopted. Then, random forest was employed to rank the importance of factors that are significant in violation prediction. The results showed that the presence of median, land use type, and number of lanes are the most significant variables in spatial violation. The findings of this study can provide a basis for traffic practitioners, researchers, and authorities to analyze the reasons for pedestrians’ spatial violations and develop guidelines for crossings design.
译文:
①本研究基于在中国上海 14 个路段进行的 15,090 个样本的现场观察,调查了行人空间违规行为的关键影响因素。应用违规预测模型预测道路几何设计和交通对违规数量的影响,并使用实时行人违规预测模型预测行人是否会发生空间违规行为。对于违规预测模型,使用了 贝叶斯泊松对数正态模型,对于实时行人违规预测模型,采用了贝叶斯逻辑回归模型。然后,采用随机森林对在违规预测中显着影响的因素的重要性进行排序。结果表明,中央分隔带的存在、土地利用类型和车道数量是空间违规行为中最显著的变量。本研究的结果可以为交通从业者、研究人员和管理部门分析行人空间违规行为的原因并制定交叉口设计指南提供依据。
高亮词汇对照
| 原文 | 译文 |
|---|---|
| critical contributing factors | 关键影响因素 |
| pedestrian spatial violations | 行人空间违规行为 |
| field observation | 现场观察 |
| roadway segments | 路段 |
| violation prediction model | 违规预测模型 |
| roadway geometry design | 道路几何设计 |
| traffic | 交通 |
| real-time pedestrian violation prediction model | 实时行人违规预测模型 |
| spatially violate | 空间违规行为 |
| Bayesian Poisson-lognormal model | 贝叶斯泊松对数正态模型 |
| Bayesian logistic regression model | 贝叶斯逻辑回归模型 |
| random forest | 随机森林 |
| violation prediction | 违规预测 |
| presence of median | 中央分隔带的存在 |
| land use type | 土地利用类型 |
| number of lanes | 车道数量 |
| significant variables | 显著的变量 |
| spatial violation | 空间违规行为 |
| traffic practitioners, researchers, and authorities | 交通从业者、研究人员和管理部门 |
| pedestrians’ spatial violations | 行人空间违规行为 |
| guidelines for crossings design | 交叉口设计指南 |
43.翻译
原文:
②The connected and automated vehicle (CAV) technologies have made great progresses. It has been commonly accepted that CV or AV technologies would reduce human errors in driving and benefit traffic safety. However, the answer of how many crashes can be prevented because of CV or AV technologies has not reached a consistent conclusion. In order to quantitatively answer this question, this study used meta-analysis to evaluate the safety effectiveness of nine common and important CV or AV technologies, and tested the safety effectiveness of these technologies for six countries. First, 73 studies about the safety impact of CV or AV technologies were filtered out from 826 CAV-related papers or reports. Second, the safety impacts of these technologies with regard to assistant types and triggering times have been compared. It shows AV technologies can play a more significant role than CV technologies, and the technologies with closer triggering time to collision time have greater safety effectiveness. Third, in the meta-analysis, the random effect model was used to evaluate the safety effectiveness, and the funnel plots and trim-and-fill method were used to evaluate and adjust publication bias, so as to objectively evaluate the safety effectiveness of each technology. Then, according to the crash data of six countries, the comprehensive safety effectiveness and compilation of safety effectiveness of the above technologies were calculated. The results show that if all of technologies were implemented in the six countries, the average number of crashes could be reduced by 3.40 million, among which the India would reduce the most (54.24%). Additionally, different countries should develop different development strategies, e.g., USA should prioritize the development of the lane change warning and intersection warning, the UK should prioritize applications related to intersection warning and rear-end warning. Overall, this study provides comprehensive and quantitative understating of the safety effectiveness of CA or AV technologies and would contribute to government, vehicle companies, and agencies in deciding the development priority of CA or AV technologies.
译文:
②联网和自动驾驶汽车 (CAV) 技术取得了巨大进展。人们普遍认为,CV 或 AV 技术将减少驾驶中的人为错误并有益于交通安全。然而,由于 CV 或 AV 技术可以避免多少起碰撞事故的答案尚未达成一致结论。为了定量地回答这个问题,本研究使用元分析来评估九种常见且重要的 CV 或 AV 技术的安全有效性,并测试了这些技术在六个国家/地区的安全有效性。首先,从 826 篇CAV 相关论文或报告中筛选出 73 项关于 CV 或 AV 技术的安全影响的研究。其次,比较了这些技术在辅助类型和触发时间方面的安全影响。结果表明,AV 技术比 CV 技术发挥更大的作用,并且触发时间更接近碰撞时间的技术具有更大的安全有效性。第三,在元分析中,使用随机效应模型评估安全有效性,并使用 漏斗图和 trim-and-fill 方法评估和调整发表偏倚,以便客观地评估每种技术的安全有效性。然后,根据六个国家/地区的碰撞数据,计算了上述技术的综合安全有效性和安全有效性汇总。结果表明,如果在六个国家/地区实施所有技术,则平均碰撞次数可以减少 340 万次,其中印度将减少最多(54.24%)。此外,不同的国家/地区应制定不同的发展策略,例如,美国应优先发展车道变换警告和交叉路口警告,英国应优先发展与交叉路口警告和追尾警告相关的应用程序。总的来说,本研究提供了对 CA 或 AV 技术的安全有效性的全面和定量的理解,并将有助于政府、汽车公司和机构决定 CA 或 AV 技术的发展重点。
高亮词汇对照
| 原文 | 译文 |
|---|---|
| connected and automated vehicle (CAV) technologies | 联网和自动驾驶汽车 (CAV) 技术 |
| CV or AV technologies | CV 或 AV 技术 |
| human errors in driving | 驾驶中的人为错误 |
| traffic safety | 交通安全 |
| meta-analysis | 元分析 |
| safety effectiveness | 安全有效性 |
| safety impact | 安全影响 |
| CAV-related papers or reports | CAV 相关论文或报告 |
| assistant types and triggering times | 辅助类型和触发时间 |
| AV technologies | AV 技术 |
| CV technologies | CV 技术 |
| closer triggering time to collision time | 触发时间更接近碰撞时间 |
| random effect model | 随机效应模型 |
| funnel plots and trim-and-fill method | 漏斗图和 trim-and-fill 方法 |
| publication bias | 发表偏倚 |
| crash data | 碰撞数据 |
| comprehensive safety effectiveness | 综合安全有效性 |
| compilation of safety effectiveness | 安全有效性汇总 |
| lane change warning | 车道变换警告 |
| intersection warning | 交叉路口警告 |
| rear-end warning | 追尾警告 |
| comprehensive and quantitative understating | 全面和定量的理解 |
| CA or AV technologies | CA 或 AV 技术 |
| development priority | 发展重点 |
44.翻译
原文:
③The one-way carsharing system has been widely used in the carsharing field due to its flexibility. However, one of its main disadvantages is the imbalance between supply and pickup demand. At present, multi-source data are available for the real-time prediction of pickup demand. The multi-source data that are used for this purpose include real-time user application log data, historical order data, real-time station data, and user characteristic data. Based on these data, a demand prediction model was used to predict in real-time whether there is a pickup demand, and a demand time prediction model was applied to forecast the time at which a sharing vehicle is needed. Finally, a case study was conducted using 10 stations’ one-week field data to test the benefits of the models. The potential application of this study would effectively guide the system to formulate an active operation optimisation strategy to meet users’ demand.
译文:
③单向汽车共享系统因其灵活性已在汽车共享领域得到广泛应用。然而,其主要缺点之一是供需不平衡。目前,有多源数据可用于实时预测取车需求。用于此目的的多源数据包括实时用户应用程序日志数据、历史订单数据、实时站点数据和用户特征数据。基于这些数据,使用需求预测模型来实时预测是否存在取车需求,并应用需求时间预测模型来预测需要共享车辆的时间。最后,使用 10 个站点为期一周的现场数据进行了案例研究,以测试这些模型的优势。这项研究的潜在应用将有效地指导系统制定主动运营优化策略以满足用户的需求。
高亮词汇对照
| 原文 | 译文 |
|---|---|
| one-way carsharing system | 单向汽车共享系统 |
| carsharing field | 汽车共享领域 |
| imbalance between supply and pickup demand | 供需不平衡 |
| multi-source data | 多源数据 |
| real-time prediction of pickup demand | 实时预测取车需求 |
| real-time user application log data | 实时用户应用程序日志数据 |
| historical order data | 历史订单数据 |
| real-time station data | 实时站点数据 |
| user characteristic data | 用户特征数据 |
| demand prediction model | 需求预测模型 |
| pickup demand | 取车需求 |
| demand time prediction model | 需求时间预测模型 |
| case study | 案例研究 |
| field data | 现场数据 |
| active operation optimisation strategy | 主动运营优化策略 |
45.翻译
原文:
④As electric bicycles (e-bikes) are becoming popular in China, concerns have been raised about their safety conditions. A traffic conflict technique is commonly used in traffic safety analysis, and there are many conflict measures designed for cars. However, e-bikes have high flexibility to change speed and trajectories, which is different from cars, so the conflict measures defined for e-bikes need to be independently explored. Based on e-bike driving characteristics, this paper proposes a new measure, the Integrated Conflict Intensity (ICI), for traffic conflicts involving e-bikes at intersections. It measures the degree of dangerousness of a conflict process, with consideration of both conflict risk and conflict severity. Time to collision is used to measure the conflict risk. Relative kinetic energy is used to measure the conflict severity. ICI can be calculated based on video analysis. The method of determining ICI thresholds for three conflict levels (serious, less serious, and slight) and two conflict types (conflicts between two e-bikes, and conflicts between an e-bike and a car) is put forward based on the questionnaires about safety perception of e-bike riders, which is regarded as the criterion of e-bike safety conditions at intersections. The video recording and a questionnaire survey about conflicts involving e-bikes at intersections have been conducted, and the unified thresholds applicable to different intersections have been determined. It is verified that ICI and its thresholds meet the criterion of e-bike safety conditions. This work is expected to be used in the selection of intersections for safety improvement of e-bike traffic.
译文:
④由于电动自行车(e-bikes)在中国越来越受欢迎,人们对其安全状况的担忧也日益增加。交通冲突技术通常用于交通安全分析,并且有许多为汽车设计的冲突衡量指标。然而,电动自行车具有改变速度和轨迹的高度灵活性,这与汽车不同,因此需要独立探索为 电动自行车定义的冲突衡量指标。本文基于 电动自行车驾驶特性,提出了一种新的衡量指标,即综合冲突强度 (ICI),用于衡量交叉路口涉及电动自行车的交通冲突。它衡量了冲突过程的危险程度,同时考虑了冲突风险和冲突严重程度。碰撞时间用于衡量冲突风险。相对动能用于衡量冲突严重程度。ICI 可以基于视频分析进行计算。基于关于电动自行车骑行者安全感知的问卷调查,提出了确定三种冲突级别(严重、不太严重和轻微)和两种冲突类型(两辆 电动自行车之间的冲突以及一辆 电动自行车与一辆汽车之间的冲突)的 ICI 阈值的方法,该方法被认为是交叉路口电动自行车安全状况的标准。已经进行了视频记录和关于交叉路口涉及电动自行车的冲突的问卷调查,并且已经确定了适用于不同交叉路口的统一阈值。经验证,ICI 及其阈值符合电动自行车安全状况的标准。预计这项工作将用于选择交叉路口以改善电动自行车交通的安全。
高亮词汇对照
| 原文 | 译文 |
|---|---|
| electric bicycles (e-bikes) | 电动自行车(e-bikes) |
| safety conditions | 安全状况 |
| traffic conflict technique | 交通冲突技术 |
| traffic safety analysis | 交通安全分析 |
| conflict measures | 冲突衡量指标 |
| e-bikes | 电动自行车 |
| high flexibility to change speed and trajectories | 改变速度和轨迹的高度灵活性 |
| e-bike driving characteristics | 电动自行车驾驶特性 |
| Integrated Conflict Intensity (ICI) | 综合冲突强度 (ICI) |
| traffic conflicts involving e-bikes | 电动自行车的交通冲突 |
| degree of dangerousness | 危险程度 |
| conflict process | 冲突过程 |
| conflict risk | 冲突风险 |
| conflict severity | 冲突严重程度 |
| Time to collision | 碰撞时间 |
| Relative kinetic energy | 相对动能 |
| video analysis | 视频分析 |
| ICI thresholds | ICI 阈值 |
| conflict levels | 冲突级别 |
| conflict types | 冲突类型 |
| questionnaires about safety perception of e-bike riders | 关于电动自行车骑行者安全感知的问卷调查 |
| criterion of e-bike safety conditions | 电动自行车安全状况的标准 |
| video recording | 视频记录 |
| questionnaire survey | 问卷调查 |
| selection of intersections for safety improvement of e-bike traffic | 选择交叉路口以改善电动自行车交通的安全 |